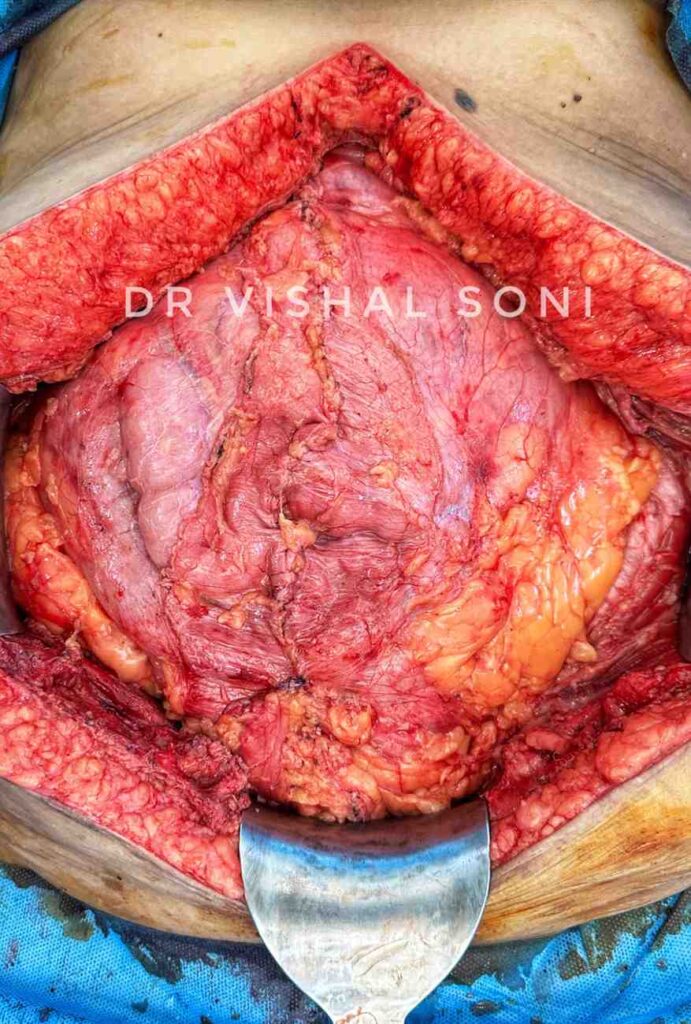
Component Separation Surgery
Component separation surgery, also known as Abdominal Wall Reconstruction (AWR), is a complex surgical procedure that is used to repair large, complex & recurrent abdominal wall defects. These defects can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, infection, tumors, or previous surgeries. The surgery involves separating and moving the various components of the abdominal wall in order to close the defect.
The abdominal wall is made up of several layers of muscle and tissue, including the external oblique, internal oblique, transversus abdominis, and rectus abdominis muscles. These muscles work together to support the organs in the abdomen and protect them from injury. When there is a defect in the abdominal wall, these muscles may be weakened or damaged, making it difficult to maintain the proper structure and function of the abdomen.
Component separation surgery is typically performed in a hospital under general anesthesia. During the procedure, the surgeon will make incisions in the abdomen and carefully separate the various layers of muscle and tissue. The surgeon will then use sutures or mesh to close the defect and reposition the muscles and tissue to restore the strength and integrity of the abdominal wall.
One of the most important aspects of component separation surgery is preserving the blood supply & Nerve Supply to the muscles and tissue. The surgeon must be careful to avoid damaging the blood vessels that supply the muscles, as this can lead to complications such as tissue necrosis or infection. In some cases, the surgeon may need to use tissue flaps to provide additional blood supply to the repaired area.
Recovery from component separation surgery can be a lengthy process and patients will need to follow a strict post-operative plan to ensure proper healing. This may include bed rest, pain management, and physical therapy to help restore strength and mobility to the abdominal muscles.
Component separation surgery is a complex and challenging procedure that requires specialized training and expertise. It is typically reserved for patients with large or complex abdominal wall defects who have not responded to other treatments. While the surgery carries risks, including bleeding, infection, and complications related to anesthesia, it can be highly effective in restoring the function and structure of the abdominal wall and improving overall quality of life.